🤔 自定义指令 - 让程序听懂你的话!
🎯 学习目标
准备好让你的程序变得更智能了吗?今天我们要学习如何向程序发送复杂数据!🚀
你将掌握:
- 📦 理解 Solana 的数据格式
- 🔧 使用 Borsh 序列化数据
- 📨 发送自定义指令
- 🎮 构建真实应用场景
🌟 为什么这很重要?
掌握自定义指令 = 解锁无限可能!
- 从简单的 "Ping" → 复杂的游戏逻辑
- 从固定操作 → 动态交互
- 从玩具项目 → 生产级应用
🎭 第一章:理解 Solana 的独特架构
🏗️ 程序 vs 数据的分离哲学
让我们通过一个生动的比喻理解 Solana 的设计:
🏢 传统智能合约(如 Ethereum)
├── 📝 代码逻辑
└── 💾 存储数据
→ 所有东西都在一起(像一体机)
🏗️ Solana 架构
├── 🤖 程序账户(只有逻辑)
│ └── "我是计算器,只会算数"
└── 📦 数据账户(只有数据)
└── "我存储所有的数字"
→ 分工明确(像专业团队)

💡 设计优势
为什么要分离?
- ⚡ 并行处理:多个程序可同时读取同一程序
- 🔄 可升级性:升级程序不影响数据
- 💰 成本效率:只为需要的数据付费
- 🚀 性能优化:减少不必要的数据加载
📊 数据流动示意
📧 第二章:指令数据的奥秘
🔢 什么是 8 位数据?
让我们用一个形象的比喻:
人类语言: "装备剑"
↓ 翻译
计算机语言: [01000101, 01110001, 01110101]
↑ ↑ ↑
装备 剑ID 玩家ID
🎯 为什么要用字节数组?
| 方式 | 示例 | 传输大小 | 处理速度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ❌ JSON | {"action":"equip","item":123} | 30 字节 | 慢(需解析) |
| ❌ XML | <action>equip</action> | 50 字节 | 更慢 |
| ✅ 字节数组 | [0x01, 0x7B] | 2 字节 | 极快! |
🚀 性能对比
字节数组让 Solana 快 100倍!
- 无需解析 JSON
- 直接读取内存
- 最小传输开销
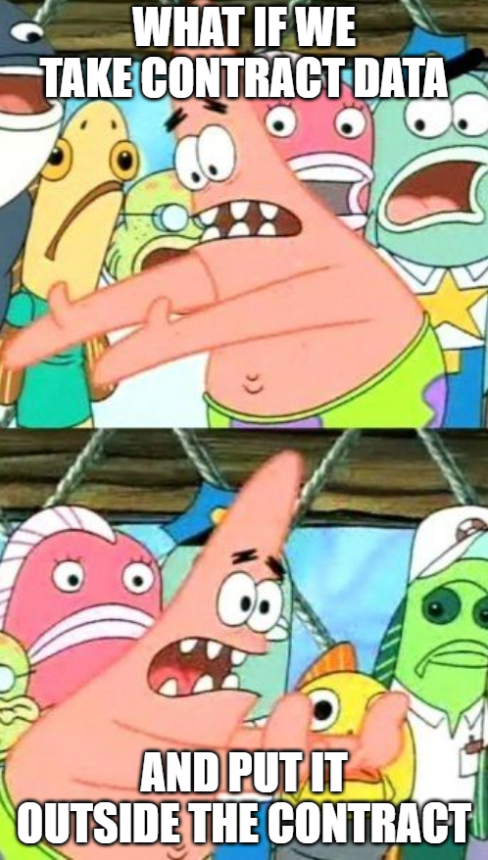
📦 交易结构详解
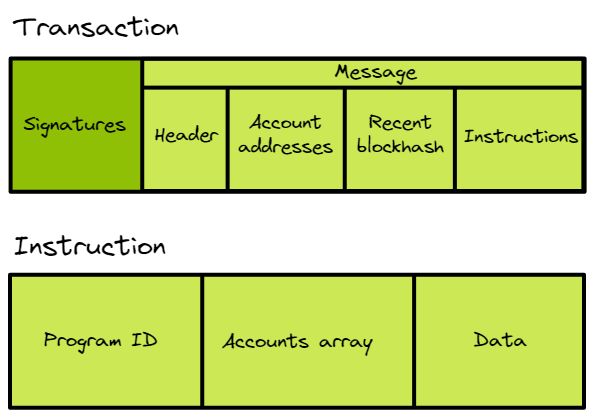
// 🎨 一个交易的完整画面
const transaction = {
// 可以有多个指令(批量操作)
instructions: [
{
programId: "游戏程序地址", // 调用谁
accounts: ["玩家", "物品库"], // 涉及谁
data: [0x01, 0x02, 0x03] // 说什么
},
{
programId: "代币程序地址",
accounts: ["玩家钱包", "商店"],
data: [0x04, 0x05]
}
]
}
🔨 第三章:Borsh 序列化实战
🎯 什么是序列化?
序列化就像打包行李 🧳:
📦 打包过程(序列化)
原始数据 → 压缩 → 标准格式 → 字节数组
🎁 解包过程(反序列化)
字节数组 → 解析 → 还原 → 原始数据
🛠️ 安装 Borsh
# 安装 Borsh 库
npm install @project-serum/borsh
📝 实战示例:游戏装备系统
让我们创建一个完整的游戏装备系统:
// 📁 gameInstructions.ts
import * as Borsh from "@project-serum/borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
// 🎮 Step 1: 定义指令类型
enum GameInstruction {
EquipItem = 0, // 装备物品
UnequipItem = 1, // 卸下物品
UpgradeItem = 2, // 升级物品
TradeItem = 3 // 交易物品
}
// 📊 Step 2: 定义数据结构
interface EquipItemData {
instruction: number; // 指令类型
playerId: number; // 玩家 ID
itemId: number; // 物品 ID
slot: number; // 装备槽位
}
// 🗺️ Step 3: 创建序列化模式
const EquipItemSchema = Borsh.struct([
Borsh.u8("instruction"), // u8 = 无符号 8 位整数 (0-255)
Borsh.u32("playerId"), // u32 = 无符号 32 位整数
Borsh.u32("itemId"),
Borsh.u8("slot")
]);
// 🔧 Step 4: 序列化函数
export function createEquipInstruction(
playerId: number,
itemId: number,
slot: number
): Buffer {
// 📦 准备数据
const data: EquipItemData = {
instruction: GameInstruction.EquipItem,
playerId,
itemId,
slot
};
// 🎯 创建缓冲区(预留足够空间)
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(100);
console.log("📏 初始缓冲区大小:", buffer.length);
// 🔨 编码数据
EquipItemSchema.encode(data, buffer);
// ✂️ 裁剪到实际大小
const instructionBuffer = buffer.slice(
0,
EquipItemSchema.getSpan(buffer)
);
console.log("✅ 最终数据大小:", instructionBuffer.length);
console.log("📊 数据内容:", instructionBuffer.toString('hex'));
return instructionBuffer;
}
// 🎯 使用示例
const equipData = createEquipInstruction(
1001, // 玩家 ID
5678, // 物品 ID (比如:炎魔剑)
2 // 装备槽 (比如:主手)
);
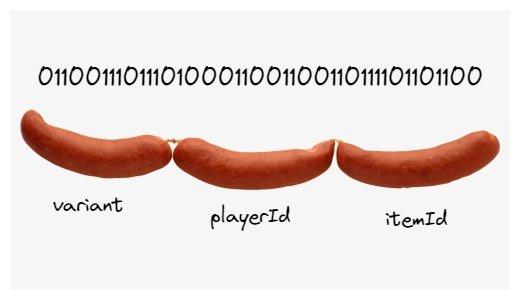
🎨 可视化序列化过程
原始数据:
{
instruction: 0, // EquipItem
playerId: 1001,
itemId: 5678,
slot: 2
}
↓ Borsh.encode()
字节数组(十六进制):
[00] [E9 03 00 00] [2E 16 00 00] [02]
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
指令 玩家ID 物品ID 槽位
就像切香肠一样精确!🌭
💻 第四章:完整实战 - 发送自定义指令
🎮 构建游戏交易
// 📁 sendGameTransaction.ts
import {
Connection,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
PublicKey,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
Keypair,
clusterApiUrl
} from '@solana/web3.js';
import { createEquipInstruction } from './gameInstructions';
// 🎯 游戏程序 ID(示例)
const GAME_PROGRAM_ID = new PublicKey(
"GameProgramID111111111111111111111111111111"
);
async function equipItemTransaction() {
console.log("🎮 开始装备物品...");
// 🌐 Step 1: 连接网络
const connection = new Connection(
clusterApiUrl('devnet'),
'confirmed'
);
// 🔑 Step 2: 准备账户
const player = Keypair.generate(); // 实际中从钱包获取
const playerDataAccount = new PublicKey("玩家数据账户");
const itemDataAccount = new PublicKey("物品数据账户");
const gameStateAccount = new PublicKey("游戏状态账户");
// 📦 Step 3: 创建指令数据
const instructionData = createEquipInstruction(
1001, // 玩家 ID
5678, // 炎魔剑 ID
2 // 主手槽位
);
// 🏗️ Step 4: 构建指令
const instruction = new TransactionInstruction({
programId: GAME_PROGRAM_ID,
// 🔑 账户列表(顺序很重要!)
keys: [
{
pubkey: player.publicKey,
isSigner: true, // 玩家需要签名
isWritable: false // 不修改玩家账户
},
{
pubkey: playerDataAccount,
isSigner: false, // 数据账户不签名
isWritable: true // 需要写入装备信息
},
{
pubkey: itemDataAccount,
isSigner: false,
isWritable: true // 更新物品状态
},
{
pubkey: gameStateAccount,
isSigner: false,
isWritable: true // 更新游戏状态
}
],
// 📨 自定义数据!
data: instructionData
});
// 📮 Step 5: 创建交易
const transaction = new Transaction().add(instruction);
console.log("📤 发送交易...");
console.log("📊 数据大小:", instructionData.length, "字节");
try {
// 🚀 Step 6: 发送并确认
const signature = await sendAndConfirmTransaction(
connection,
transaction,
[player] // 签名者
);
console.log("✅ 装备成功!");
console.log("🔗 交易签名:", signature);
console.log(`🔍 查看: https://explorer.solana.com/tx/${signature}?cluster=devnet`);
return signature;
} catch (error) {
console.error("❌ 装备失败:", error);
throw error;
}
}
// 🎮 执行
equipItemTransaction().then(sig => {
console.log("🎊 游戏操作完成!");
}).catch(err => {
console.error("😢 游戏操作失败:", err);
});
🎨 前端集成示例
// 📁 components/GameActions.tsx
import { useWallet, useConnection } from '@solana/wallet-adapter-react';
import { createEquipInstruction } from '../utils/gameInstructions';
export function GameActions() {
const { publicKey, sendTransaction } = useWallet();
const { connection } = useConnection();
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const handleEquipItem = async (itemId: number, slot: number) => {
if (!publicKey) {
alert("请先连接钱包!");
return;
}
setLoading(true);
try {
// 创建指令数据
const data = createEquipInstruction(
12345, // 玩家 ID(从游戏状态获取)
itemId,
slot
);
// 构建交易
const transaction = new Transaction().add(
new TransactionInstruction({
programId: GAME_PROGRAM_ID,
keys: [/* ... */],
data
})
);
// 发送交易
const signature = await sendTransaction(
transaction,
connection
);
// 等待确认
await connection.confirmTransaction(signature);
alert(`✅ 装备成功!物品 ${itemId} 已装备到槽位 ${slot}`);
} catch (error) {
alert(`❌ 装备失败: ${error.message}`);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
};
return (
<div className="game-inventory">
<h2>🎒 背包物品</h2>
<div className="items-grid">
<button
onClick={() => handleEquipItem(5678, 2)}
disabled={loading}
>
⚔️ 装备炎魔剑
</button>
<button
onClick={() => handleEquipItem(9012, 3)}
disabled={loading}
>
🛡️ 装备圣盾
</button>
</div>
{loading && <p>⏳ 处理中...</p>}
</div>
);
}
🏆 挑战任务:构建消息板应用
🎯 任务目标
创建一个链上消息板,支持:
- 📝 发布消息(包含作者、内容、时间戳)
- ❤️ 点赞消息
- 💬 回复消息
📊 数据结构设计
// 消息指令类型
enum MessageInstruction {
PostMessage = 0,
LikeMessage = 1,
ReplyMessage = 2
}
// 发布消息的数据
interface PostMessageData {
instruction: number;
content: string; // 消息内容(最多 280 字符)
timestamp: number; // 时间戳
}
// 创建序列化模式
const PostMessageSchema = Borsh.struct([
Borsh.u8("instruction"),
Borsh.str("content"), // 字符串类型
Borsh.u64("timestamp") // 64 位时间戳
]);
💡 实现提示
- 字符串处理:Borsh 的
str类型会自动处理长度 - 时间戳:使用
Date.now()获取 - 账户设计:考虑如何存储消息和用户数据
📚 深入理解
🎯 Borsh 数据类型速查
| 类型 | 说明 | 字节数 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
u8 | 无符号 8 位 | 1 | 0-255 |
u16 | 无符号 16 位 | 2 | 0-65,535 |
u32 | 无符号 32 位 | 4 | 0-4,294,967,295 |
u64 | 无符号 64 位 | 8 | 很大! |
i8 | 有符号 8 位 | 1 | -128 到 127 |
bool | 布尔值 | 1 | true/false |
str | 字符串 | 可变 | UTF-8 编码 |
[u8; N] | 固定数组 | N | N 个字节 |
🔍 调试技巧
// 🔍 查看序列化数据
function debugBuffer(buffer: Buffer, label: string) {
console.log(`\n=== ${label} ===`);
console.log("长度:", buffer.length, "字节");
console.log("十六进制:", buffer.toString('hex'));
console.log("字节数组:", Array.from(buffer));
console.log("===============\n");
}
// 使用
const data = createEquipInstruction(1001, 5678, 2);
debugBuffer(data, "装备指令数据");
⚠️ 常见陷阱和解决方案
| 问题 | 原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| "缓冲区溢出" | 分配空间不足 | 增加 Buffer.alloc() 大小 |
| "无效指令" | 数据格式错误 | 检查模式定义顺序 |
| "账户不匹配" | 账户顺序错误 | 确认程序期望的顺序 |
| "序列化失败" | 数据类型不匹配 | 使用正确的 Borsh 类型 |
🎊 总结
恭喜你掌握了自定义指令!你现在可以:
✅ 理解数据格式 - 知道为什么用字节数组 ✅ 使用 Borsh - 序列化各种数据类型 ✅ 发送复杂指令 - 不再局限于简单操作 ✅ 构建真实应用 - 游戏、DeFi、社交等
🚀 你的能力升级了!
之前:只能 Ping 一下 😅
现在:可以构建完整应用!🚀
从 $10,000 项目 → $10,000,000 项目!
下一步:学习如何在 Solana 程序中处理这些自定义指令! 🎯